
Yuri Bushkin, Ph.D.
Adjunct Professor of Medicine
bushkiyu@njms.rutgers.edu
Overview. This research program was historically focused on biology and function of MHC class I proteins in antigen presentation during infection and in tissue transplantation. Recently, our interest in the network of receptor-mediated responses provided for a renewed focus on the immunology of infectious diseases and the pathology of proinflammatory responses induced by infections. This approach is supported by the technological advances, which enable identification of single cell immunity functional signatures based on simultaneous detection of protein and RNA markers.
Focus on disease. Stimulation of T cells with specific functions (effector, memory or regulatory) through T cell receptor interactions initiates a signaling cascade that alters gene expression in responding cells. These changes can be detected by measuring expression of RNA molecules using single molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization (smFISH) and flow cytometry. The FISH-Flow detection platform can identify key markers of T cell activation defined as such due to their characteristic expression in functional signatures of T cells associated with evolution of infection and disease. In case of tuberculosis (TB), it’s a complex disease with remarkable plasticity. The progression of infection is generally moving from preclinical to active disease or to latent TB. Reactivation of latent TB to a preclinical stage and then active disease is also common due to the changes in the immune system status (cancer, HIV co-infection). The functions of most cell populations are defined by the expression of key markers, i.e., pro-inflammatory or suppressive cytokines. Thus, distinct proportions of T cell subsets expressing different biomarkers may serve as indicators of TB infection stages.
However, the function-reporting RNA signatures appear to be complex and incorporate a variety of cellular biomarkers in addition to cytokines. Advances in the field of immunometabolism indicate that a switch in bioenergetics strategy of immune cells from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis (Warburg effect) is a critical metabolic requirement for effective pro-inflammatory and anti-microbial responses. The switch leads to certain changes in the gene expression profile. Therefore, many types of immune cells, not just T cells, are likely to have metabolic signatures associated with the status of immune response. Such immunometabolic signatures could be detected by FISH-Flow at different TB infection stages.
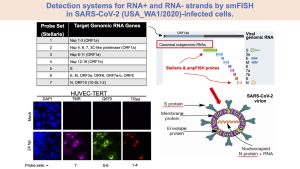
In the case of infection caused by the SARS-CoV-2, the initial proinflammatory responses induced by infection set up multi-organ pathology. This includes cardiovascular disease and exacerbation of pre-existing pathological conditions such as diabetes. The underlying mechanisms are studied in vitro and in vivo with human cell cultures and hamster-based systems, respectively, using collaborative efforts within PHRI and RBHS and with Boston University. As initial step towards the goal of investigating the mechanisms of COVID-19 pathogenesis, we established a robust fluorescence-based microscopy assay enabling multiplexed detection of SARS-CoV-2 (see Figure for anti-viral probe systems) and human or hamster host mRNAs at a single-cell resolution.
Vascular and endothelial performance during COVID-19. The pathological consequences of COVID-19 include dysregulated vascular functions associated with thrombosis. We investigated our hypothesis that certain molecular pathways ubiquitously expressed in lung tissues are associated with disruption of vascular homeostasis and ensuing prothrombotic events during infection. We found that modulations in the expression of cellular receptors involved in homeostasis and endothelial performance such as angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), CD147 and glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) are the hallmark responses induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The prothrombotic shift in infected hamster lungs was revealed by increased expression of coagulation cascade mediators TF, PLAT, PAI-1, THBD and vWF associated with endothelial dysfunction; the latter shown through the upregulated expression of ESAM, CD106, CD201, VEGF-A and VEGFR-2. These markers correlated with the modulation of ACE2, CD147 and GRP78 expression patterns and the infection states in human macrophage and hamster pulmonary infection models. Our findings suggest possible molecular pathways for exploration of novel drugs capable of blocking the prothrombotic shift events that exacerbate COVID-19 pathophysiology and control the disease.
Nisa A, Kumar R, Ramasamy S, Kolloli A, Olejnik J, Jalloh S, Gummuluru S, Subbian S, Bushkin Y (2024) Modulations of Homeostatic ACE2, CD147, GRP78 Pathways Correlate with Vascular and Endothelial Performance Markers during Pulmonary SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cells 13: 432. PMI: 38474396
Jalloh S, Olejnik J, Berrigan J, Nisa A, Suder EL, Akiyama H, Lei M, Ramaswamy S, Tyagi S, Bushkin Y, Muhlberger E, Gummuluru S (2022) CD169-mediated restrictive SARS-CoV-2 infection of macrophages induces pro-inflammatory responses. PLoS Pathog 18: e1010479. PMI: 36279285
Datta K, LaRue R, Permpalung N, Das S, Zhang S, Mehta Steinke S, Bushkin Y, Nosanchuk JD, Marr KA (2022) Development of an Interferon-Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) to Aid Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol 60: e0112822. PMI: 36190260
Badeti S, Jiang Q, Naghizadeh A, Tseng HC, Bushkin Y, Marras SAE, Nisa A, Tyagi S, Chen F, Romanienko P, Yehia G, Evans D, Lopez-Gonzalez M, Alland D, Russo R, Gause W, Shi L, Liu D (2022) Development of a novel human CD147 knock-in NSG mouse model to test SARS-CoV-2 viral infection. Cell Biosci 12: 88. PMI: 35690792
Kumar R, Singh P, Kolloli A, Shi L, Bushkin Y, Tyagi S, Subbian S (2019) Immunometabolism of Phagocytes During Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Front Mol Biosci 6: 105. PMI: 31681793
Marras SAE, Bushkin Y, Tyagi S (2019) High-fidelity amplified FISH for the detection and allelic discrimination of single mRNA molecules. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 128: 13921–13926. PMI: 31221755
Shi L, Jiang Q, Bushkin Y, Subbian S, Tyagi S (2019) Biphasic Dynamics of Macrophage Immunometabolism during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. MBio 10. PMI: 30914513
Arrigucci R, Bushkin Y, Radford F, Lakehal K, Vir P, Pine R, Martin D, Sugarman J, Zhao Y, Yap GS, Lardizabal AA, Tyagi S, Gennaro ML (2017) FISH-Flow, a protocol for the concurrent detection of mRNA and protein in single cells using fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 12: 1245-1260. PMI: 28518171
Radford F, Tyagi S, Gennaro ML, Pine R, Bushkin Y (2016) Flow Cytometric Characterization of Antigen-Specific T Cells Based on RNA and Its Advantages in Detecting Infections and Immunological Disorders. Crit Rev Immunol 36: 359-378. PMI: 28605344
Vir P, Arrigucci R, Lakehal K, Davidow AL, Pine R, Tyagi S, Bushkin Y, Lardizabal A, Gennaro ML (2015) Single-Cell Cytokine Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Cells Correlates with Latent Tuberculosis Status. PLoS One 10: e0144904. PMI: 26658491
Bushkin Y, Radford F, Pine R, Lardizabal A, Mangura BT, Gennaro ML, Tyagi S (2015) Profiling T cell activation using single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry. J Immunol 194: 836-841. PMI: 25505292
Pine R, Bushkin Y, Gennaro ML (2013) Immunological biomarkers for tuberculosis: potential for a combinatorial approach. In McFadden J, Beste D, and Kierzek A (eds.), Systems Biology of Tuberculosis. Springer, pp. 193-219.
Zhao J, Guo Y, Yan Z, Zhang J, Bushkin Y, Liang P (2011) Soluble MHC I and soluble MIC molecules: potential therapeutic targets for cancer. Int Rev Immunol 30: 35-43. PMI: 21235324
Mizrahi S, Markel G, Porgador A, Bushkin Y, Mandelboim O (2007) CD100 on NK cells enhance IFNgamma secretion and killing of target cells expressing CD72. PLoS One 2: e818. PMI: 17786190
Dong Y, Demaria S, Sun X, Santori FR, Jesdale BM, De Groot AS, Rom WN, Bushkin Y (2004) HLA-A2-restricted CD8+-cytotoxic-T-cell responses to novel epitopes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis superoxide dismutase, alanine dehydrogenase, and glutamine synthetase. Infect Immun 72: 2412-2415. PMI: 15039371
Dong Y, Lieskovska J, Kedrin D, Porcelli S, Mandelboim O, Bushkin Y (2003) Soluble nonclassical HLA generated by the metalloproteinase pathway. Hum Immunol 64: 802-810. PMI: 12878359
Haynes LD, Bushkin Y, Love RB, Burlingham WJ (2002) Interferon-gamma drives the metalloproteinase-dependent cleavage of HLA class I soluble forms from primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Hum Immunol 63: 893-901. PMI: 12368042
Mandelboim O, Lieberman N, Lev M, Paul L, Arnon TI, Bushkin Y, Davis DM, Strominger JL, Yewdell JW, Porgador A (2001) Recognition of haemagglutinins on virus-infected cells by NKp46 activates lysis by human NK cells. Nature 409: 1055-1060. PMI: 11234016

