David Dubnau, Ph.D.
Professor of Microbiology, Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics
dubnauda@njms.rutgers.edu
+1-973-854-3400
Room W410-E
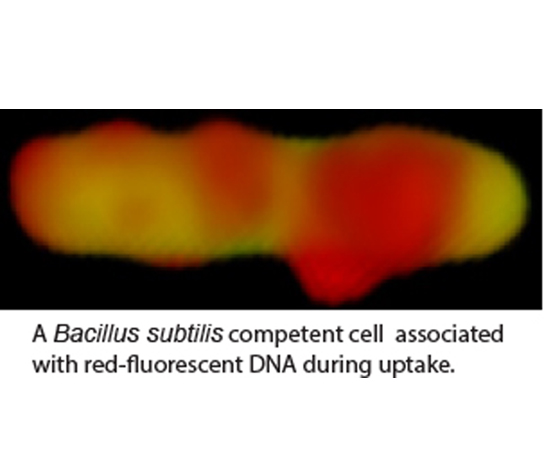
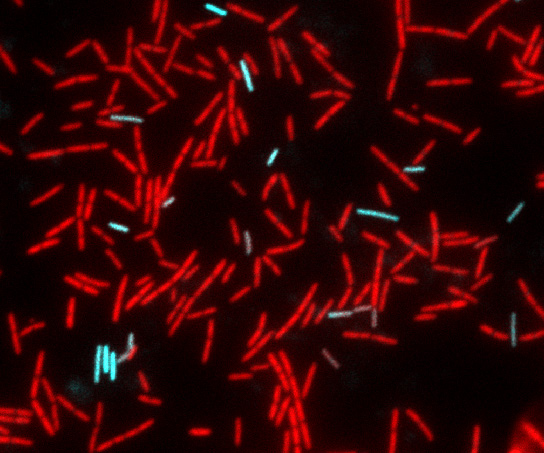
We study developmental adaptations that the model Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis uses to enhance fitness in the face of environmental challenges. For example, many bacteria take up environmental DNA in a process known as genetic transformation, which enables the cells to incorporate fitness-enhancing genes and mediates the spread of antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. To take up DNA, cells must be in a physiological state called “competence” and we have investigated the regulation of the competent state. At present, we are investigating the process of transformation itself, to understand more fully how environmental DNA is taken up into the cytoplasm of competent cells. For this we are using a combination of genetics, biochemistry, cell biology and structural biology, the latter in collaboration with Dr. M. Neiditch, here at NJMS. A second project concerns a complex of three proteins required for sporulation, biofilm formation and genetic competence that we have recently discovered. This complex carries two Fe-S clusters and in we are exploring the mechanism of action of the proteins in this complex, which have been shown in another lab to be required for the maturation of certain important RNA transcripts as well as stimulating a phosphorylation cascade that is needed for bacterial development.
Samir S Elshereef AA, Alva V, Hahn J, Eck F, Celma L, Thormann K, Dubnau D, Galperin MY, Selim KA (2025) ComFB, a new widespread family of c-di-NMP receptor proteins. PNAS: in press
Hahn J, Celma L, El-shereef A, Samir S, Dubnau E, Selim KK, Dubnau D (2025) c-di-GMP-Dependent Regulation of Motility by: comFB and comFC. bioRxiv: poste July 11
Ahmed I, Hahn J, Henrickson A, Khaja FT, Demeler B, Dubnau D, Neiditch MB (2022) Structure-function studies reveal ComEA contains an oligomerization domain essential for transformation in gram-positive bacteria. Nat Commun 13: 7724. PMI: 36513643
Hahn J, DeSantis M, Dubnau D (2021) Mechanisms of Transforming DNA Uptake to the Periplasm of Bacillus subtilis. MBio 12: e0106121. PMI: 34126763
De Santis M, Hahn J, Dubnau D (2021) ComEB protein is dispensable for the transformation but must be translated for the optimal synthesis of comEC. Mol Microbiol 116: 71-79. PMI: 33527432
Adusei-Danso F, Khaja FT, DeSantis M, Jeffrey PD, Dubnau E, Demeler B, Neiditch MB, Dubnau D (2019) Structure-Function Studies of the Bacillus subtilis Ric Proteins Identify the Fe-S Cluster-Ligating Residues and Their Roles in Development and RNA Processing. MBio 10. PMI: 31530674
Dubnau D, Blokesch M (2019) Mechanisms of DNA Uptake by Naturally Competent Bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. PMI: 31433955
Carabetta VJ, Greco TM, Cristea IM, Dubnau D (2019) YfmK is an N(epsilon)-lysine acetyltransferase that directly acetylates the histone-like protein HBsu in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116: 3752-3757. PMI: 30808761
Tanner AW, Carabetta VJ, Dubnau D (2018) ClpC and MecA, components of a proteolytic machine, prevent Spo0A-P-dependent transcription without degradation. Mol Microbiol. PMI: 29446505
Tanner AW, Carabetta VJ, Martinie RJ, Mashruwala AA, Boyd JM, Krebs C, Dubnau D (2017) The RicAFT (YmcA-YlbF-YaaT) complex carries two [4Fe-4S]2+ clusters and may respond to redox changes. Mol Microbiol 104: 837-850. PMI: 28295778
Diethmaier C, Chawla R, Canzoneri A, Kearns DB, Lele PP, Dubnau D (2017) Viscous drag on the flagellum activates Bacillus subtilis entry into the K-state. Mol Microbiol. PMI: 28800172
Miras M, Dubnau D (2016) A DegU-P and DegQ-Dependent Regulatory Pathway for the K-state in Bacillus subtilis. Front Microbiol 7: 1868. PMI: 27920766
Dubnau EJ, Carabetta VJ, Tanner AW, Miras M, Diethmaier C, Dubnau D (2016) A protein complex supports the production of Spo0A-P and plays additional roles for biofilms and the K-state in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 101: 606-624. PMI: 27501195
Carabetta VJ, Greco TM, Tanner AW, Cristea IM, Dubnau D (2016) Temporal Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis Acetylome and Evidence for a Role of MreB Acetylation in Cell Wall Growth. mSystems 1. PMI: 27376153
Hahn J, Tanner AW, Carabetta VJ, Cristea IM, Dubnau D (2015) ComGA-RelA interaction and persistence in the Bacillus subtilis K-state. Mol Microbiol 97: 454-471. PMI: 25899641
Carabetta VJ, Tanner AW, Greco TM, Defrancesco M, Cristea IM, Dubnau D (2013) A complex of YlbF, YmcA and YaaT regulates sporulation, competence and biofilm formation by accelerating the phosphorylation of Spo0A. Mol Microbiol 88: 283-300. PMI: 23490197
Mirouze N, Desai Y, Raj A, Dubnau D (2012) Spo0A~P imposes a temporal gate for the bimodal expression of competence in Bacillus subtilis. PLoS Genet 8: e1002586. PMI: 22412392
Mirouze N, Prepiak P, Dubnau D (2011) Fluctuations in spo0A transcription control rare developmental transitions in Bacillus subtilis. PLoS Genet 7: e1002048. PMI: 21552330
Briley K, Jr., Prepiak P, Dias MJ, Hahn J, Dubnau D (2011) Maf acts downstream of ComGA to arrest cell division in competent cells of B. subtilis. Mol Microbiol 81: 23-39. PMI: 21564336
Briley K, Jr., Dorsey-Oresto A, Prepiak P, Dias MJ, Mann JM, Dubnau D (2011) The secretion ATPase ComGA is required for the binding and transport of transforming DNA. Mol Microbiol 81: 818-830. PMI: 21707789
Prepiak P, Dubnau D (2007) A peptide signal for adapter protein-mediated degradation by the AAA+ protease ClpCP. Mol Cell 26: 639-647. PMI: 17560370
Maamar H, Raj A, Dubnau D (2007) Noise in gene expression determines cell fate in Bacillus subtilis. Science 317: 526-529. PMI: 17569828
Maamar H, Dubnau D (2005) Bistability in the Bacillus subtilis K-state (competence) system requires a positive feedback loop. Mol Microbiol 56: 615-624. PMI: 15819619
Hahn J, Maier B, Haijema BJ, Sheetz M, Dubnau D (2005) Transformation proteins and DNA uptake localize to the cell poles in Bacillus subtilis. Cell 122: 59-71. PMI: 16009133
Draskovic I, Dubnau D (2005) Biogenesis of a putative channel protein, ComEC, required for DNA uptake: membrane topology, oligomerization and formation of disulphide bonds. Mol Microbiol 55: 881-896. PMI: 15661011
Albano M, Smits WK, Ho LT, Kraigher B, Mandic-Mulec I, Kuipers OP, Dubnau D (2005) The Rok protein of Bacillus subtilis represses genes for cell surface and extracellular functions. J Bacteriol 187: 2010-2019. PMI: 15743949
Turgay K, Hahn J, Burghoorn J, Dubnau D (1998) Competence in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by regulated proteolysis of a transcription factor. EMBO J 17: 6730-6738. PMI: 9890793
Narayanan CS, Dubnau D (1987) An in vitro study of the translational attenuation model of ermC regulation. J Biol Chem 262: 1756-1765. PMI: 3027098
Dubnau D (1985) Induction of ermC requires translation of the leader peptide. EMBO J 4: 533-537. PMI: 4018035
Hahn J, Grandi G, Gryczan TJ, Dubnau D (1982) Translational attenuation of ermC: a deletion analysis. Mol Gen Genet 186: 204-216. PMI: 6810064
Shivakumar AG, Dubnau D (1981) Characterization of a plasmid-specified ribosome methylase associated with macrolide resistance. Nucleic Acids Res 9: 2549-2562. PMI: 6792593